Guide for sustainability as the new digital revolution for business
August 22, 2023 / 7 min read

Photo by Ricardo Arce on Unsplash
Table of contents
Sustainability in the IT world has become a growing trend and for some good reasons. It's not just about reducing the environmental impact of digital tasks; it can also save costs, boost reputation, and build lasting resilience. Sounds good, doesn't it?
The Sustainability revolution in IT
The green shift in IT refers to the growing awareness and implementation of environmentally friendly practices within the IT industry. This movement aims at reducing the environmental impact of IT operations, products and services while promoting resource efficiency and minimising waste.
The implications of embracing sustainability in IT are far-reaching, but it can be overwhelming to know where to start.
Key aspects
Here, it is important to mention several important questions. Energy efficiency is vital for businesses as it allows them to reduce costs, meet regulatory requirements, and achieve sustainability goals. This can be accomplished by cutting energy consumption in data centres and IT infrastructure.
Next, sustainable design principles that prioritise user experience and minimise resource consumption not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance customer satisfaction.
 Photo by John Cameron on Unsplash
Photo by John Cameron on Unsplash
Proper e-waste management ensures that businesses mitigate environmental consequences and comply with waste management regulations.
Green procurement is also important. It’s based on selecting IT products and services that prioritise sustainability, support environmentally conscious suppliers and lead to cost savings through energy-efficient solutions. Adopting remote work and digital collaboration tools reduces the need for physical office space and commuting-related emissions. Transitioning to cloud-based services and utilising virtualisation minimises energy consumption and physical infrastructure, resulting in cost savings and more efficient resource allocation.
Finally, implementing energy-efficient algorithms, modular code, and open-source solutions in software development reduces energy consumption and waste. All of that is contributing to a greener future.
In short, by embracing the green/sustainability revolution in IT, businesses can not only minimise their environmental impact but also reap the benefits of cost savings, improved customer relationships, and long-term resilience.
“Sustainability is the path to a more efficient, innovative, and profitable business.”
Environmental impact of technology and the internet
Websites impact the environment!
An average website produces 1.76g of CO2 for every page view, so a site with 100,000 page views per month emits 2 112kg of CO2 every year. [1] As you can see, although it's not obvious, websites have a direct effect on the environment!
- Websites are responsible for 3.7% of global greenhouse emissions (the result similar to the airline industry), this includes the carbon footprint of the internet and gadgets and systems supporting it [2]
- Data centres are estimated to be responsible for up to 3% of global electricity consumption today and are projected to touch 4% by 2030. [3]
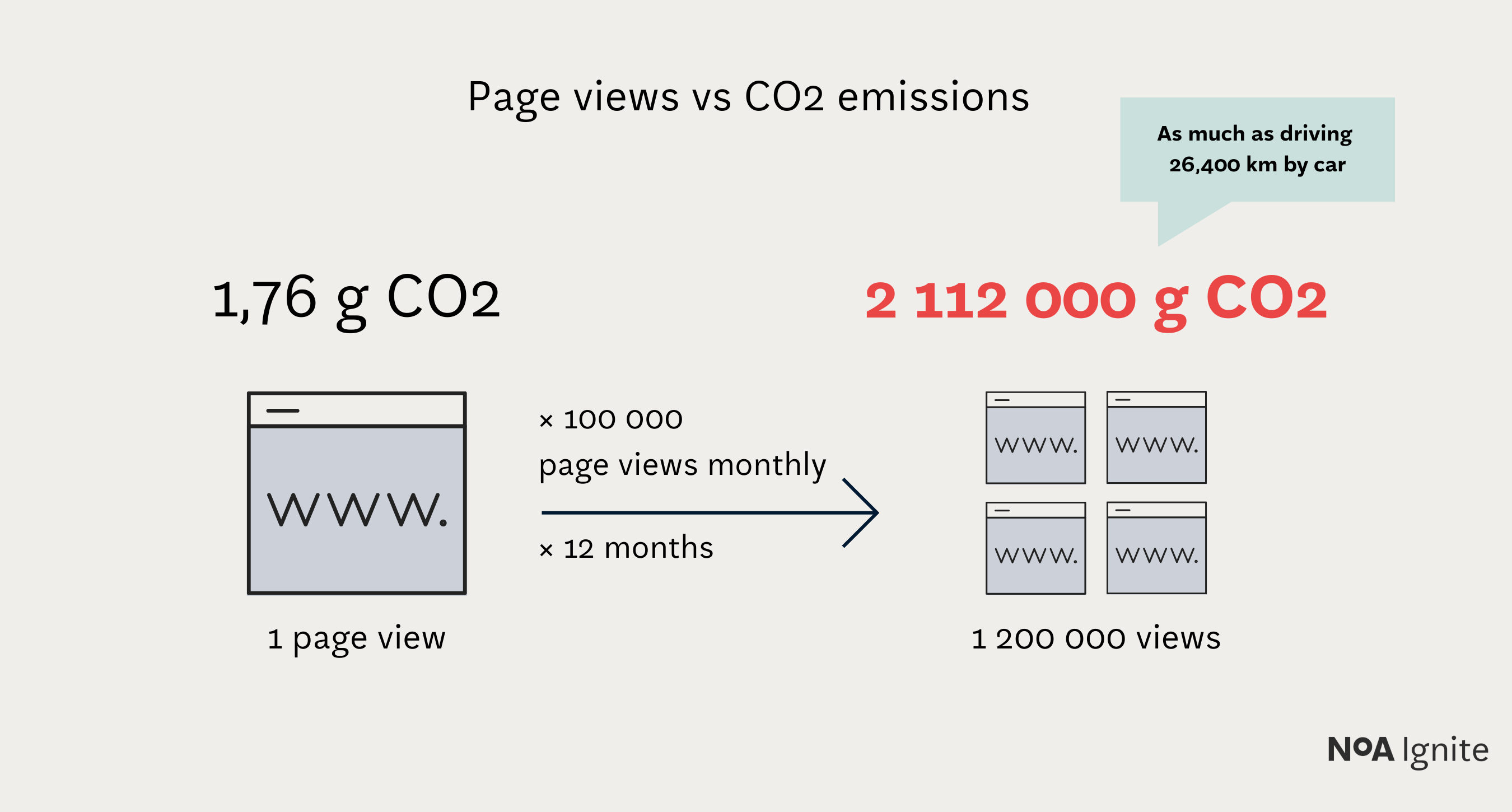 Page views vs CO2 emissions
Page views vs CO2 emissions
E-waste disposal
The disposal of e-waste entails challenges due to the volume of waste generated and the complexity and cost of the recycling process. The truth is improper disposal can lead to environmental damage. Hazardous materials in e-waste can leach into soil and water, polluting the environment and posing a health risk to humans and wildlife. E-waste also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
“The disposal of e-waste is an emerging global environmental and public health issue, as this waste has become the most rapidly growing segment of the formal municipal waste stream worldwide.”
Thankfully, e-waste can be relatively easily managed through waste management methods such as recycling, incineration, and data destruction.
Avoiding greenwashing
What is greenwashing?
Greenwashing is one of the hottest topics recently. You surely know that not all companies are committed to sustainability. As a result, greenwashing, a marketing tactic used by large companies to falsely present their products as environmentally friendly, has become an issue. By using misleading or exaggerated claims about the environmental benefits of their products, companies can mislead consumers into making purchasing choices that are not truly eco-friendly.
“In reality, every company with a green claim is greenwashing,” says sustainability consultant JD Capuano. “Our current economic system is based on unlimited growth, but our resources are limited. Even a company that makes the most responsible products can still have significant environmental impact.”
Be transparent
Transparency leads to strong relationships with customers and the whole society. People are increasingly interested in the environmental and social impacts of the companies behind the products and services they use. Transparency and accountability can help your business identify areas for improvement, track progress and make necessary adjustments to ensure that sustainability initiatives in your company are both effective and impactful.
Third-party certifications and audits
The truth is any statement your brand makes about sustainability and eco-friendliness should be provable. That’s what third-party certifications and audits are for. However, you must be careful and pick only those certifications that have a good reputation in the industry and actually prove something. Many certificates look nice but are issued to any company that’s ready to pay for them. Don’t go this way!
“... a third-party certification such as ISO 17024, EPt(GHG), or those offered by CSA Group (..) will ensure quality and that your inventory is complete, consistent, and transparent.”
Green solutions in design
Sustainable design principles aim to minimise the environmental impact of products and services throughout their entire lifecycle, from production to disposal. By incorporating these principles into the design and development of digital products, we can reduce their ecological footprint, conserve resources and mitigate climate destruction.
Here’s what you should do:
Energy efficiency
Design digital products to consume less energy during their operation, which can be achieved by optimising software algorithms, utilising energy-saving hardware and encouraging energy-saving user behaviours. Energy-efficient digital products can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production.
Material reduction
Design digital products with minimal material usage and focus on lightweight designs. This can involve reducing packaging materials, using fewer components and optimising hardware designs. Material reduction helps conserve resources and reduce waste generation.
Resource efficiency
Make use of renewable resources, such as solar or wind energy, to power digital products. Additionally, utilise recycled and recyclable materials in product manufacturing. This principle helps conserve natural resources and reduce waste generation.
Moreover, you should design digital products to be long-lasting and robust to minimise the need for frequent replacements. This can be achieved by using high-quality materials, promoting modularity and offering repair services. Durability helps reduce resource consumption and waste production in the long run.
 Photo by Tyler Casey on Unsplash
Photo by Tyler Casey on Unsplash
Upgradeability
Create digital products that can be easily upgraded, either through hardware or software updates. This enables the product to stay relevant and functional for a longer period, reducing the need for users to purchase new products frequently.
End-of-life management
Consider how digital products will be disposed of or recycled at the end of their lifecycle. Design products that can be easily disassembled and provide guidelines for recycling and safe disposal. This helps minimise e-waste and the associated environmental impact.
 Photo by Jack Church on Unsplash
Photo by Jack Church on Unsplash
User-centred design
Develop digital products that cater to user needs and preferences while minimising their environmental impact. Educate users on sustainable practices and promote energy-saving behaviours, such as reducing screen brightness, enabling power-saving modes and unplugging devices when not in use.
Eco-innovation
Constantly explore new ways to minimise the environmental impact of digital products. This can involve investing in research and development, collaborating with stakeholders, and adopting best practices from other industries.
“With the Internet playing an increasingly important role in the daily lives of billions of people, there is a moral imperative for our community to address these issues and make creating more sustainable digital products and services something that's easy for everyone to understand and implement.”
Green solutions in development
Energy-efficient algorithms and data structures
Utilising energy-efficient algorithms and data structures in software development has become increasingly important in the context of green solutions in IT development. This is because the environmental impact of the IT sector, including energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, has been growing rapidly due to the increasing demand for digital products and services. Implementing energy-efficient algorithms and data structures can contribute to a more sustainable IT landscape thanks to reduced energy consumption and better code performance.
Modular and reusable code
Modular and reusable code plays a significant role in promoting sustainability in software development. Reusable code is often subject to more extensive testing and debugging as it is used in multiple applications or projects. This can result in higher-quality code with fewer defects, reducing the need for time-consuming and energy-intensive debugging processes. Moreover, by creating easily maintainable, extensible and reusable code, developers can reduce software's environmental impact while improving its overall quality and efficiency.
Working with IT companies to achieve sustainability
The role of IT companies in promoting sustainable practices
All IT companies should focus on:
- Designing energy-efficient hardware and software,
- Implementing SaaS solutions and cloud computing to reduce physical IT infrastructure,
- Using renewable energy sources
When it comes to software development and DevOps, IT companies can prioritise sustainable practices such as designing software to minimise resource consumption and implementing continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) processes to streamline software development. All of that contributes to reducing e-waste.
Selecting partners that prioritise sustainability
Before you decide to work with a given IT company, ask them about their approach to sustainability.
What solutions and practices do they have in place to promote eco-friendliness?
Can they assist you in making your company more sustainable?
If so, what is their role in this process like? Getting answers to these questions can help you make more informed decisions.
“By choosing partners that prioritise sustainability, companies can amplify their positive impact on the environment and drive change within their industry.”
Conclusion
By prioritising sustainability in the design, development and operation of all your digital technologies, you can reduce the environmental impact and carbon footprint of the digital revolution and strive towards a more sustainable future.
If you feel like implementing the changes mentioned in this article is something you can’t handle on your own, we’re happy to help! You can book a free consultation below:
Bibliography
[1] Delle Chan, "Your website is killing the planet" in WIRED UK, 22 March 2021 [wired.co.uk/article/internet-carbon-footprint];
[2] "The carbon footptint of the internet" in Climate Impact Partners, 22 April 2021 [climateimpact.com/news-insights/insights/infographic-carbon-footprint-internet/];
[3] Marcus Law, "Energy efficiency predictions for data centres in 2023" in Data Centre, 30 December 2022 [datacentremagazine.com/articles/efficiency-to-loom-large-for-data-centre-industry-in-2023#];
[4] Tim Frick, “Designing for Sustainability: A Guide to Building Greener Digital Products and Services” 2016, Oreilly Media;
Author

Mateusz Różalski
Senior UX Designer
Mateusz is a designer with many years of experience and a background in music. He feels most identified with the role of a product designer. Not only is he great at UX and UI design, but he also excels in business analysis and communication with developers.
Related articles
![optimizely CMS 12 mockup: content types]()
April 23, 2024 / 5 min read
What benefits you get by upgrading to Optimizely CMS 12
Many of you are no doubt contemplating the advantages of upgrading to Optimizely CMS 12. This article presents the benefits, from technical improvements to the strategic business and...
![Photo of an IT team looking into a monitor.]()
April 8, 2024 / 4 min read
Best practices for Optimizely CMS 12 upgrade
Making the move from Optimizely CMS 11 to 12 is no walk in the park; thankfully, we’ve written a guide on the best practices for efficiently upgrading.